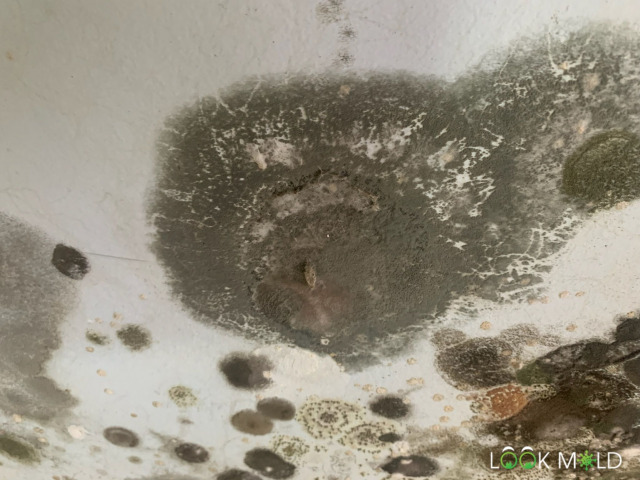
As a professional mold inspector, people often call me in a panic:
“I have Black Mold!”
Black mold, also known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a greenish-black fungus that grows on water-damaged materials like drywall, wood, and insulation. It may produce mycotoxins, which can affect indoor air quality and trigger symptoms like coughing, sneezing, fatigue, or headaches. For people with asthma or compromised immune systems, those effects can be more serious.
TL;DR – Key Facts About Black Mold
- Grows on wet drywall, wood, and wallpaper glue
- May release mycotoxins that irritate lungs and sinuses
- Can spread behind walls and through HVAC
- Identifying the mold species requires lab testing
- Small spots? You might clean it yourself
- Large or hidden mold? Call a pro
But here’s the thing:
Not all black-colored mold is toxic, and not all toxic molds are black. That’s why it’s critical to have the mold identified properly and fixed fast before it spreads or impacts your health.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
Step by Step: How to Remove Black Mold Yourself (Under 10 Square Feet)
- Put on PPE (gloves, goggles, N95).
- Seal off the work area with plastic sheeting.
- Lightly mist mold to prevent spores becoming airborne.
- Scrub with vinegar or peroxide.
- Remove caulk or porous materials that cannot be cleaned.
- HEPA vacuum the area.
- Run fans or dehumidifier to fully dry the space.
- Fix the moisture source immediately.
What Is Black Mold?
Let’s clear something up about black mold.
You’ve probably heard the name Stachybotrys chartarum, that’s the technical term, but most people just call it black mold. It’s the dark, slimy stuff that shows up when water damage sticks around too long, usually on drywall, wood, or wallpaper glue.
Under the right conditions (moisture + time + organic material), it thrives, especially in warm, humid spaces.
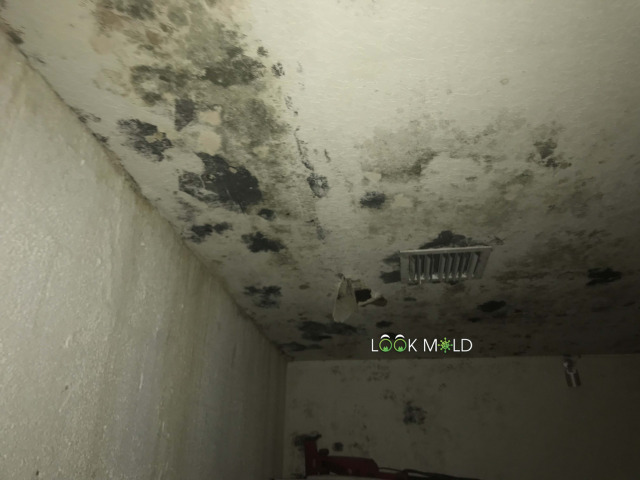

Does Black Mold Make You Sick?
Here’s the deal:
- Black mold can produce mycotoxins, chemicals that sound scary (and sometimes are).
- Most healthy people might experience allergy-like symptoms:
- Sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, maybe a skin rash
- But for those with:
- Asthma
- Mold allergies
- Compromised immune systems
Symptoms can be much more serious
Bottom line? Black mold exists in nature, it helps break down dead plant material outdoors.
But when it creeps into your home and hides behind walls? That’s a problem worth dealing with.
The Science Behind It
Stachybotrys chartarum is a slow-growing fungus that thrives on cellulose-rich materials like:
- Drywall
- Wood framing
- Insulation paper or wallpaper
It needs constant moisture to survive, think roof leaks, plumbing drips, or flood damage.
Stachybotrys may produce mycotoxins, which can affect your air quality and cause health symptoms if inhaled over time.
While it usually looks dark green or black and slimy, under dry conditions it can turn grayish and powdery.
“Black mold” isn’t a scientific term, it’s a media label used to describe dark molds that might be toxic.
The only way to confirm the species is through lab testing.
Fun Fact
There are more than 365,000 known types of mold, and many of them,
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
What Causes Black Mold in Homes?
Black mold doesn’t just appear out of nowhere, it needs moisture, organic material, and time. Here are the most common culprits that create the perfect environment for it to grow:
Common Moisture Sources:
- Roof or plumbing leaks
(Often hidden inside walls or ceilings) - Basement flooding
(Especially in older homes or areas with poor drainage) - Poor ventilation / HVAC condensation
(Common in attics, bathrooms, and ductwork) - Window or door seal failure
(Allows rainwater to seep inside wall cavities) - Crawl spaces with standing water or poor drainage
Did you know?
Mold can begin growing in just 24 to 48 hours when humidity is high.
Source: FEMA
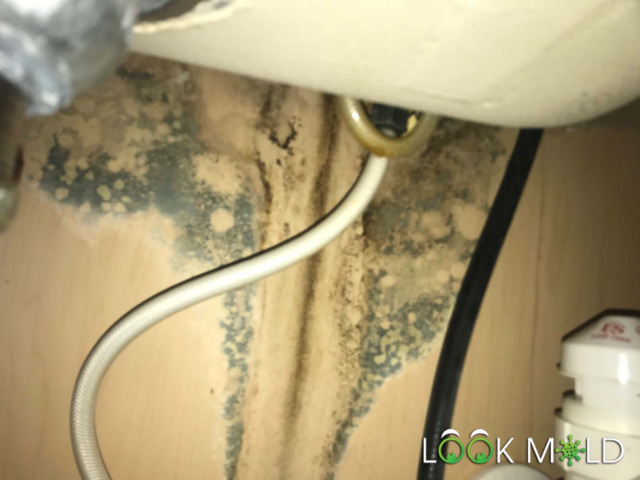

What Does Black Mold Look Like?
When wet, black mold may appear slimy and dark, like someone used a black or green crayon. When dried out, it becomes powdery or chalky, and may flake when disturbed.
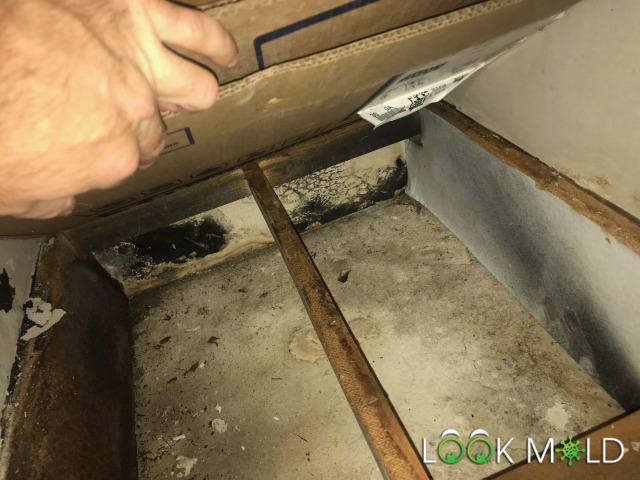

What Harmless Black Mold Looks Like
Some molds appear black but do not produce mycotoxins. These include:
| Appearance | Possible Species | Toxic? |
|---|---|---|
| Dry and sooty black | Cladosporium | Usually not |
| Fuzzy, blackish blue | Alternaria | Low risk |
| Slick and slimy | Stachybotrys chartarum | Possibly toxic |
Identification should be done by a qualified lab or professional inspector.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
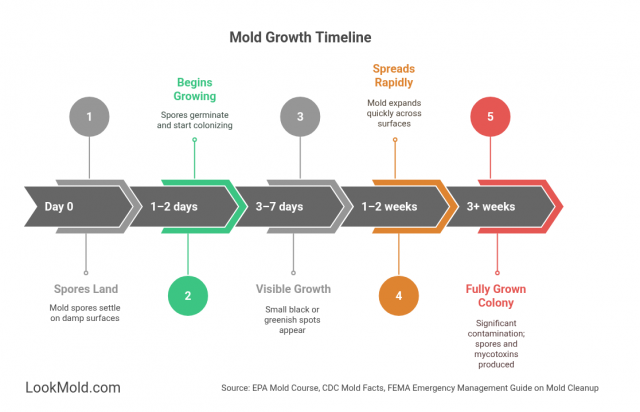
Black Mold Growth Timeline
Here’s how black mold develops over time once moisture is present:
| Timeframe | Stage | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Day 1–2 | Spore Landing | Mold spores land on damp organic material (e.g., drywall) |
| Day 3–7 | Colonization Begins | Hyphae grow into the surface and begin feeding |
| Week 2 | Visible Mold Forms | Black or dark green colonies start to appear |
| Week 3+ | Sporulation & Spread | Mold releases spores into the air, potentially affecting other rooms |
Source: NYC DOH Guidelines on Mold
Black Mold vs. Other Toxic Molds
While Stachybotrys chartarum (black mold) gets most of the attention, it’s not the only dangerous mold you might find indoors. Several other species can also release harmful mycotoxins and thrive in damp environments.
Here’s how black mold compares to other toxic molds:
| Mold Type | Where It Grows | Potential Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Stachybotrys (Black Mold) | Wet drywall, insulation, ceilings | Mycotoxins, respiratory issues, memory problems |
| Chaetomium | Water-damaged drywall and wallpaper | Allergic reactions, neurological symptoms |
| Memnoniella | Wet wood, paper, drywall | Similar effects to black mold; respiratory irritation |
| Fusarium | Carpets, fabrics, HVAC systems | Eye infections, gastrointestinal issues, immune impacts |
| Penicillium & Aspergillus | Dust, walls, furniture, insulation, food | Asthma, allergies, and exposure to Ochratoxins |
Did you know? Some species like Aspergillus are common in indoor air and can be especially dangerous for people with weakened immune systems.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
What Does Black Mold Smell Like?
Black mold produces a distinct, musty, earthy odor caused by microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs), gases released during the mold’s digestive process.
What Are MVOCs?
MVOCs are airborne chemicals created when mold breaks down materials like wood, drywall, and paper. These gases carry the characteristic “moldy” smell and can irritate eyes, nose, and throat, even at low levels.
Common MVOCs include:
- Geosmin – smells like wet soil
- Hexanone – like sharp glue or acetone
- Octen-3-ol – like mushrooms
You might recognize the smell of mold before you see it, especially behind walls or under floors.
What Black Mold Smells Like to People
| Description | Common Comparison |
|---|---|
| Musty | Old basement, damp attic |
| Earthy | Wet soil or rotting leaves |
| Sharp & chemical-like | Paint thinner, ammonia |
| Stale | Wet towels left for days |
The smell is often stronger after rain, in humid rooms, or when the HVAC kicks on.
Odor ≠ Safety
Just because you can (or can’t) smell it doesn’t mean you’re safe:
- Some toxic molds have little to no smell.
- MVOCs can linger even after visible mold is gone.
- Hidden mold behind drywall or cabinets may only be detectable by odor.
Action Step
If you notice a persistent musty odor, especially near walls, vents, or crawlspaces, have your home professionally inspected. Mold can exist in hidden cavities long before it becomes visible.
How Does Black Mold Grow?
Black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) isn’t random, it needs the right conditions to grow and spread indoors. Think of it like a recipe:
Ingredients for Mold Growth:
- Excess moisture or water damage
(From leaks, spills, flooding, or trapped condensation) - Relative humidity over 60%
(Especially in basements, crawl spaces, and bathrooms) - Organic materials like:
- Drywall
- Wallpaper glue
- Wood and subflooring
- Cardboard or paper products
If all three of these are present for more than 24–48 hours, black mold can begin to colonize.

Is Black Mold in the Shower Dangerous?
Usually not, but it depends where the mold is growing.
Mold on shower tiles or grout is often:
- Cladosporium
- Aspergillus
These are common surface molds that are generally not toxic, though they can still cause irritation for people with mold sensitivities.
But mold behind walls, under fiberglass tubs, or inside caulking?
That’s where Stachybotrys (toxic black mold) could be hiding, and that’s a bigger concern.
If your bathroom smells musty or you’ve had a leak behind the wall, it’s worth investigating.

⏱ How Fast Does Black Mold Grow?
Mold doesn’t need much time to become a problem, especially in damp, enclosed spaces.
Growth Timeline:
- As fast as 13 days under ideal conditions
(constant moisture, warmth, poor airflow) - More commonly: 3–6 weeks
(especially when leaks go unnoticed inside walls or under flooring)
The longer moisture sits, the higher the risk of toxic mold growth.
Source: IICRC S520
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
Can Black Mold Become Airborne?
Yes, and that’s one of the reasons it can spread without you even seeing it.
How It Happens:
- When mold dries out, it releases lightweight spores
- These spores can become airborne during:
- Cleaning or disturbance
- HVAC system cycling
- Air drafts or fans
Once airborne, spores attach to dust and can travel to other rooms, landing on carpets, clothing, and furniture.
Important:
Wet mold tends to stay put. But dry mold = high risk of airborne contamination.
How Do You Identify Black Mold?
You can’t always tell what type of mold you’re dealing with just by looking at it , lab testing is key.
What a Certified Mold Inspector Does:
- Swab Samples – collected from visible mold on surfaces
- Air Samples – taken from different rooms to measure airborne spores
- Bulk Samples – small pieces of drywall, insulation, or other materials
These samples are sent to a certified lab, where a microbiologist examines them to confirm the mold species and spore concentration.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
Can You Clean Black Mold Yourself?
That depends on two things: how big the problem is, and what kind of mold you’re dealing with.
DIY Mold Cleanup (Safe in Small Areas)
If the moldy area is under 10 square feet, and you’re not dealing with toxic mold, you might be able to clean it up yourself. Here’s what you need:
- Proper PPE, gloves, N95 mask, goggles
- A non-toxic cleaner (like vinegar or hydrogen peroxide)
- Ventilation and time to fully dry the space
But remember, just wiping the surface isn’t enough. You’ve got to remove the moisture source or it’ll come right back.
Call a Professional If:
- The affected area is larger than 10 sq. ft
- You suspect Stachybotrys chartarum (black mold)
- Mold is inside walls, ceilings, or HVAC systems
The EPA recommends hiring a professional for large or potentially toxic mold problems.
Source: EPA - Mold Cleanup
How to Safely Remove Black Mold
If you’re dealing with confirmed black mold, especially behind walls or in your HVAC. DIY is not the answer. Here’s what pros do:
- Set up containment zones with negative air pressure
- Remove and discard mold-contaminated materials (not just clean them)
- Use HEPA air scrubbers and vacuums to clean the air
- Perform post-remediation testing to verify it’s safe
Professionals follow strict protocols like:
- NYC Department of Health Mold Guidelines
- IICRC S520 Mold Remediation Standard
Bottom line? You don’t want to risk spreading spores, let trained pros handle it right.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
What Does It Cost to Remove Black Mold?
Mold remediation isn’t cheap, but neither is risking your health.
Here’s what typical removal might cost:
- Crawl space: ~$1,800
- Bathroom wall: ~$2,000
- HVAC system: $3,000–$6,000
- Full room (10x12): $1,500 to $5,000+
Some insurance policies cover mold under a “fungi” or water damage clause, check with your provider.
Is My Home Safe After Mold Removal?
Yes , if remediation was done right.
Make sure:
- All contaminated materials were completely removed
- A third-party clearance test confirms the air is clean
Don’t just take someone’s word for it, ask for test results.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
Health Effects of Black Mold
Not everyone reacts to mold the same way, but here are the most common symptoms of exposure:
- Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath
- Brain fog, chronic fatigue
- Sinus pressure, headaches, itchy eyes
- Rashes, dizziness, nausea
If symptoms improve when you leave the home, that’s a strong clue that indoor mold could be the cause.
Can Black Mold Harm Pets?
Absolutely. Pets, especially dogs and cats, can be even more sensitive than humans. Symptoms may include:
- Lethargy or vomiting
- Breathing trouble
- Loss of appetite
If your pet’s acting “off” and you suspect mold at home, call a vet and check your indoor air quality.
How Do You Diagnose Mold Exposure?
There’s no one-size-fits-all test, but here’s how professionals evaluate it:
- Blood antibody testing (IgG, IgE)
- Urine mycotoxin tests (less reliable, but still used)
- Review of exposure history and symptoms
Work with a doctor trained in environmental medicine, not all physicians are mold-literate.
Can Black Mold Sickness Be Treated?
Yes, but first, you have to get out of the exposure zone.
Treatment may include:
- Removing yourself from the moldy environment
- Detoxing with supplements or medications (doctor-supervised)
- Supporting your immune system with diet, rest, and clean air
Many people feel better within days or weeks of getting out of the mold, but recovery timelines vary.
- Free phone consultation
- Local licensed remediation teams
- Available 24/7
Black Mold FAQ
Can you sleep in a room with black mold?
You can, but you really shouldn’t. Sleeping in a moldy room means you’re breathing in spores for 6–8 hours straight. That’s when people start waking up with headaches, stuffy noses, fatigue, or worse. If you’ve got asthma or mold sensitivity? Even more reason to get it checked out and cleaned up.
Does insurance cover black mold?
Sometimes yes, sometimes no. If the mold came from a covered event like a burst pipe or storm damage, you’re likely covered. But if it’s from neglect, ongoing humidity, or poor ventilation? Most policies won’t touch it. Look for a “fungi” clause or mold endorsement in your coverage.
⏳ How long does it take to get sick from mold?
It depends on your body and how bad the exposure is. Some people start sneezing, coughing, or feeling foggy within a day or two. Others take weeks. People with asthma, allergies, or weakened immune systems tend to react faster and more severely.
What kills black mold permanently?
The only permanent solution is professional remediation. That means:
- Cutting out moldy materials
- Scrubbing the air with HEPA filters
- Fixing the moisture source that caused it in the first place
You can use vinegar or hydrogen peroxide on small spots, but unless you stop the moisture? It’ll just come back.
Is black mold poisonous?
It can be. Stachybotrys chartarum, the “classic” black mold, produces mycotoxins that can be harmful, especially in high or prolonged exposure. But not all black molds are toxic, and not all toxic molds are black. Color alone isn’t enough to know.
Is black mold actually dangerous?
Yes, especially if it’s growing in places where you’re breathing it in daily, like inside walls, air vents, or a damp basement. Over time, that kind of exposure can lead to anything from allergy symptoms to serious respiratory or neurological issues.
What is black mold called?
The one everyone worries about is called Stachybotrys chartarum. But molds like Cladosporium and Alternaria can also look black and are often confused with it. You won’t know which is which without lab testing.
Why are black molds dangerous?
Because they check all the wrong boxes:
- They can release toxic mycotoxins
- They grow in hidden spots where you don’t see them
- They mess with your health slowly, sometimes without obvious symptoms
If you ignore it, it gets worse.
What are black mold symptoms in humans?
Most common symptoms look like allergies:
- Sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes
- Skin irritation or rash
- Fatigue, brain fog
- Trouble breathing or asthma flare-ups
People with asthma or immune issues may see more severe effects over time.
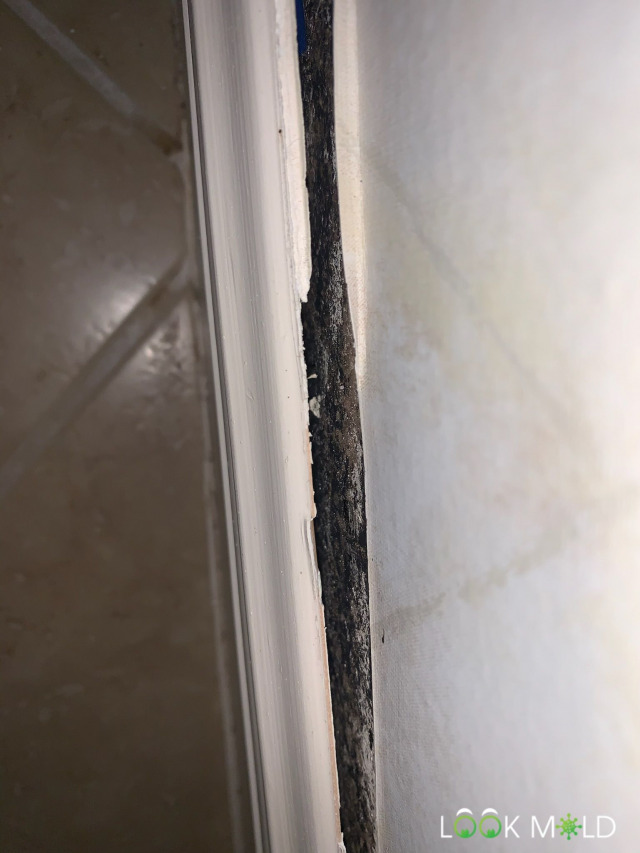
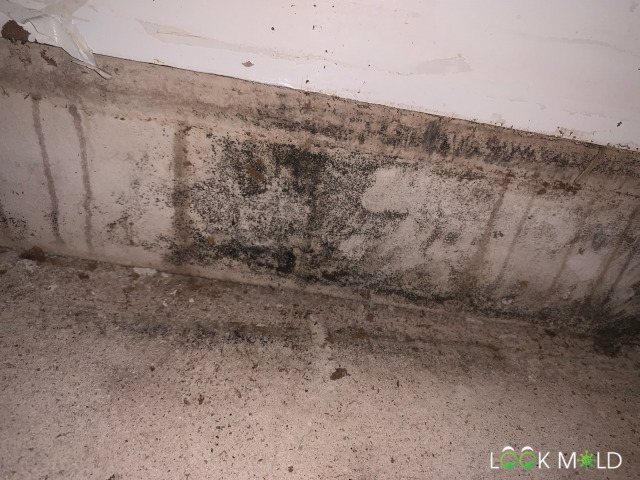
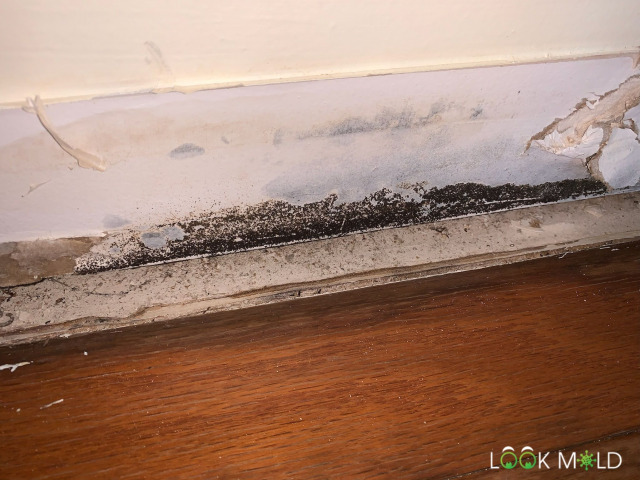
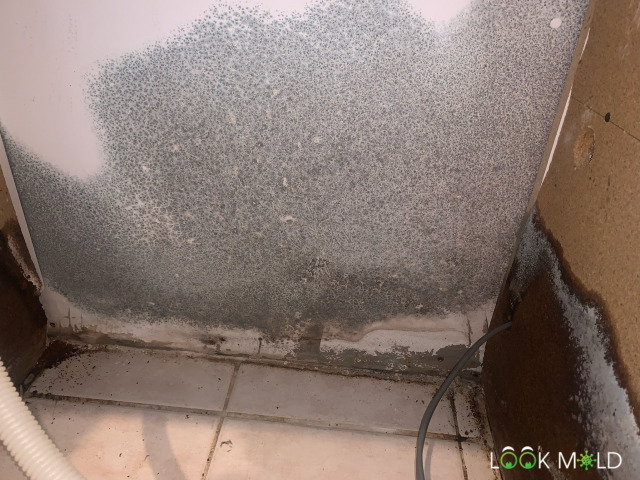
Got any black mold identification photos?
Absolutely. Here’s what it usually looks like:
Wet black mold often looks dark green and slimy. When it dries out, it gets powdery and gray. But looks can be deceiving, if you’re unsure, have it tested or bring in a licensed mold inspector.
Got More Questions About Black Mold?
You’re now equipped with facts, visuals, and real answers, no hype, no fear tactics.
If you think black mold is growing in your home, don’t wait. Confirm it, clean it, and get your air back.





